An unprecedented 1,640 CEOs departed in 2019 and now execs are dumping stock at the highest pace since 2006. A recent article in Wall Street on Parade examined the effects of CEOs exiting big corporations on their stock value.
The following is taken from a recent article by Pam Martens and Russ Martens, from August 27, 2020 ~
A rather fascinating picture is emerging that suggests that things were not as rosy in the U.S. economic landscape prior to the pandemic as President Donald Trump and his Director of the National Economic Council, Larry Kudlow, would have the public believe.
Challenger, Gray & Christmas, Inc. has been tracking CEO departures for the past 12 years. Its Vice President, Andrew Challenger, called the numbers for 2019 “staggering.” It was the highest number since their surveys began in 2002. A total of 1,640 CEOs headed for the exits last year. That was 156 more CEOs than those who left their post in 2008 – the year that Wall Street blazed a scorched earth trail through the U.S. economy.
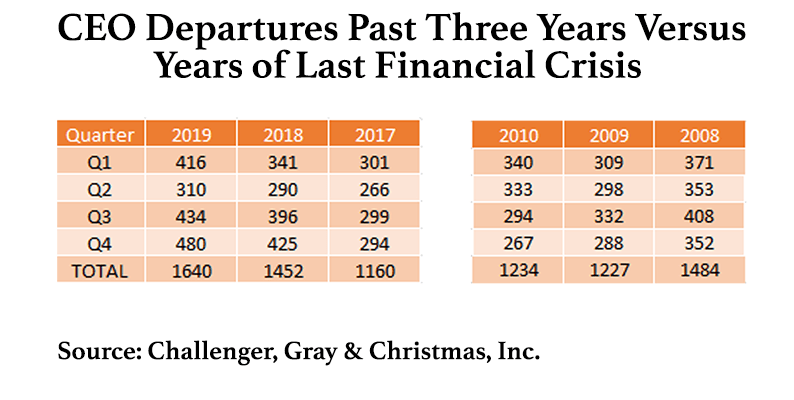
The number of CEOs that did not leave on their own accord last year was 101 out of the 1,640. According to the study, 15 CEOs left over allegations of professional misconduct; 20 left amid a scandal, “typically under investigations for financial wrongdoing or other legal issues”; 24 saw their positions terminated; 39 left due to a merger or acquisition; 3 left due to bankruptcy.
CEOs of old, established companies have the clearest view of what is happening in the overall economy. They can compare sales growth to prior years and prior decades. They can spot negative or positive trends in the economy far ahead of the economic reports that the federal government releases to the public.
When an outsized number of CEOs decide to cash out their stock options, grab their golden parachutes, and flee their corner offices – something smells.
On top of that fishy smell comes a report from TrimTabs Investment Research that corporate insiders have reaped more than $50 billion in stock sales since May, putting insider selling on a pace not seen since 2006 – two years before the stock market and economic crash of 2008.
The above two reports on corporate executive behavior are compatible with Wall Street On Parade’s reports that show that the current financial crisis began in the fall of 2019 – months before the first case of COVID-19 had emerged anywhere in the world. What triggered the financial crisis? The same kind of liquidity crisis on Wall Street that ushered in the crisis of 2008.
Why does it matter when the financial crisis began? It’s critically important for the following reasons.
First, the U.S. national debt has exploded to $26.69 trillion. To wrap your mind around this explosion of the national debt, you need some historical perspective. At the beginning of the Bill Clinton Presidency in January 1993, the U.S. national debt stood at $4 trillion. At that point, the United States was more than 200 years old. During that 200 years, the U.S. had financed the Revolutionary War, the Civil War, World Wars I and II, and the Vietnam War. The country had also been through the greatest economic collapse in its history, the Great Depression, which required a multitude of fiscal spending programs.
It took more than two centuries for the U.S. national debt to reach $4 trillion but in just the past 27 years the national debt has grown by more than $22 trillion – more than a five-fold increase in less than three decades.
This staggering amount of debt puts the nation at risk of a future credit downgrade and cripples its ability to adequately deal with the financial struggles of its citizens during the worst health and financial crisis in a century.
One of the key reasons for this mushrooming debt was the Wall Street financial crisis of 2008 which required massive fiscal spending to keep the economy from sinking into a depression.
But no serious steps were taken by Congress to reform Wall Street. Derivatives remain largely unregulated. Dark Pools are still trading in darkness. Wall Street continues to pay credit rating agencies to rate their toxic debt piles. Off-balance sheet casinos run rampant at the largest Wall Street banks. Obscene pay for performance via stock options continues to incentivize CEOs and CFOs to massage earnings.
The biggest unaddressed problem is the critical need to restore the Glass-Steagall Act. All of the dangers cited above can and do, bring down an entire financial institution as we learned in 2008. But with the restoration of the Glass-Steagall Act, the giant, federally-insured, deposit-taking banks would be completely separated from the Wall Street casino investment banks.
This handful of megabanks that hold the majority of deposits in this country are too critical to keeping credit flowing to businesses and consumers to be run by the Wall Street bet-the-ranch mentality. These banks are simply too big to be bailed out again.
When Citigroup was disintegrating from all of the evils mentioned above from 2007 to 2010, this is what it took to resuscitate its sinking hull: $45 billion in capital infusions from the U.S. Treasury; over $300 billion in asset guarantees from the federal government; the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) guaranteed $5.75 billion of its senior unsecured debt and $26 billion of its commercial paper and interbank deposits; and the Federal Reserve secretly, with no authorization or even awareness of Congress, made a cumulative $2.5 trillion in below-market-rate loans to Citigroup from 2007 through at least the middle of 2010, according to an audit by the Government Accountability Office (GAO).
And, finally, acknowledging that this latest financial crisis began prior to the pandemic shines a bright light on the incompetency of the Federal Reserve to manage these Wall Street behemoth banks. It’s simply an insane regulatory model to have a bank regulator with the ability to create money out of thin air that can secretly create and spend $29 trillion bailing out the banks to cover up its own incompetency. That’s what happened from 2007 to 2010 and is in the process of happening again.
If you find yourself relying on banks and the stock market for your retirement and savings, you may want to take out of what banks and billionaires do themselves to safeguard their assets and that’s investing in gold. Most banks have a large portion of their funds invested in gold. There’s a reason for that. Gold has stood the test of time, being a popular hedge against inflation. In the past 20 years alone, it has increased by 500%. Since the 2008 crash, it has risen by 250% and in the past few months alone since the March 2020 lockdown due to the spread of Covid-19, it has surged another 30% to beat its all-time record, surpassing $2000 and expected to reach $2500 by 2021.
Most recently, Gold has gotten increased popularity when billionaire Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway exited 26% of their funds from banks and invested $565 Million into gold. With the current economic turmoil, health crisis, rising unemployment, looming bank collapse, and… well, these unprecedented times will take a bit to recover from and it’s clearly up to each of us individually and collectively to look out for our best interests for the safety of our savings and retirement.


 Gold Products
Gold Products Silver Products
Silver Products Platinum
Platinum